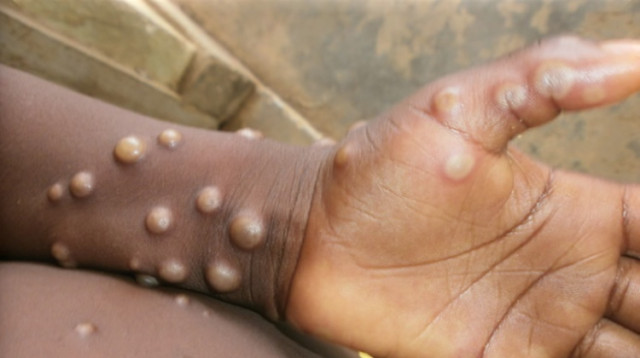
As the world confronts the Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) outbreak, the President of the Nigerian Association of Resident Doctors, Dr Dele Abdullahi, has emphasised the need for crowd management at hospitals to prevent the spread of the disease.
Abdullahi noted that crowd control in healthcare facilities should be considered a critical measure to mitigate transmission, as hospitals are potential hotspots.
The NARD president explained that one of the primary modes of the disease transmission is through crowds within hospitals, highlighting the risk of infection if someone with the disease visits the facility.
This, according to, calls for crowd control at hospitals as the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention reported 40 confirmed Mpox cases out of 830 suspected cases in the country.
Mpox continues to spread in Africa and parts of Europe, with cases reported in multiple countries. The Africa Centre for Disease Control has declared a public health emergency due to the growing mpox outbreak on the continent, particularly in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The World Health Organisation emphasised that the emergence and rapid spread of a new virus strain, clade 1b, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, which appears to be spreading primarily through sexual networks, and its detection in neighbouring countries, are particularly concerning, leading to the declaration of a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.
So far, around 2,863 confirmed monkeypox cases and 517 deaths have been reported across 13 African countries in 2024 alone.
In response to the widespread infectious disease, the NARD president suggested that hospitals should limit the number of patients and visitors, ensure proper ventilation, and enforce strict infection control protocols.
He said, "Implementing crowd control measures in hospitals can reduce the risk of transmission and prevent the spread of the disease. The new strain of mpox is more violent than previous strains, so increased awareness, improved research, and heightened alertness at border patrols are necessary to combat its spread.
"Awareness campaigns, community engagement, and reinforcing infectious disease control principles like limiting contact, frequent handwashing, and face masks are crucial to effectively combat Mpox.
"Rigorous border controls and health screenings are essential to prevent the introduction and spread of Mpox. Controlling crowds, especially in hospitals, is crucial to limit transmission. Educating the public on avoiding contaminated meat is key.
Raising awareness about early symptoms and promoting vaccination are critical to controlling the outbreak of this rare viral disease."